Zooplankton  of Mid-Atlantic Estuarine & Coastal Waters of Mid-Atlantic Estuarine & Coastal WatersMillersville University Department of Biology on NatureAtlas.org©
Identify by ShapeUse this interactive, illustrated key to identify the type of zooplankton you have. This key begins with many entry points that you can choose based on the general shape of the organism. The pages that follow provide photographs and descriptions of the zooplankton types that fit those shapes. You may have a salp or doliolid.Salps and doliolids are thaliaceans of phylum Chordata. Thaliaceans are characterized by muscular bands across the width of the body. Below are some thaliaceans commonly found in this region. Doliolids (Doliolid Thaliaceans)Doliolids (barrel-shaped) are smaller than salps with more complicated lifecycle alternating between solitary individuals (oozooids) which develop tails that bud filter feeding gastrozooids, and phorozooids which produce gonozooids. Gonozooids sexually reproduce a tailed larva which grows into the solitary individuals to complete the cycle. Dolioletta gegenbauri(gonozooid: coiled gut, 8 muscle bands, & no tail) 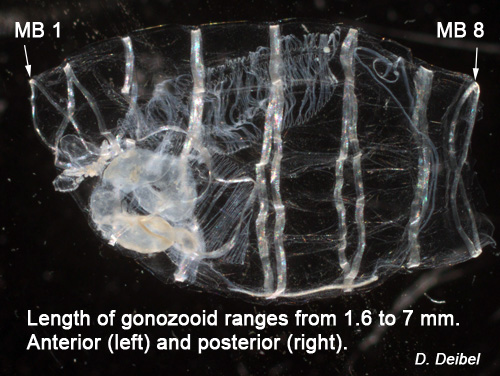
Dolioletta gegenbauri(nurse w/ zooids on tail) 
Dolioletta gegenbauri(closeup of tail w/ zooids) 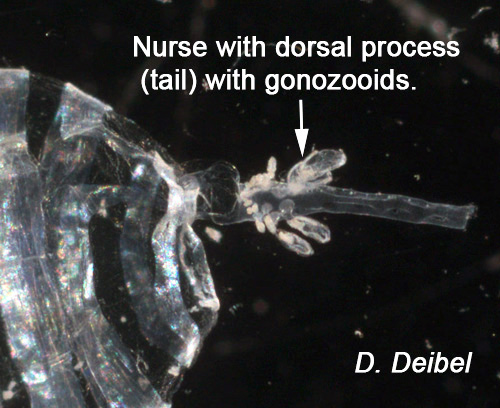
Salps (Salp Thaliaceans)Salps (meaning "bag-shaped") have lifecycles which alternate between solitary individuals which asexually reproduce chains of individuals, which sexually reproduce the solitary individuals. Due to their asexual reproduction, salps can increase rapidly. Salps are distinguished from doliolid thaliaceans by their non-parallel muscle bands. Thalia democratica(solitary) 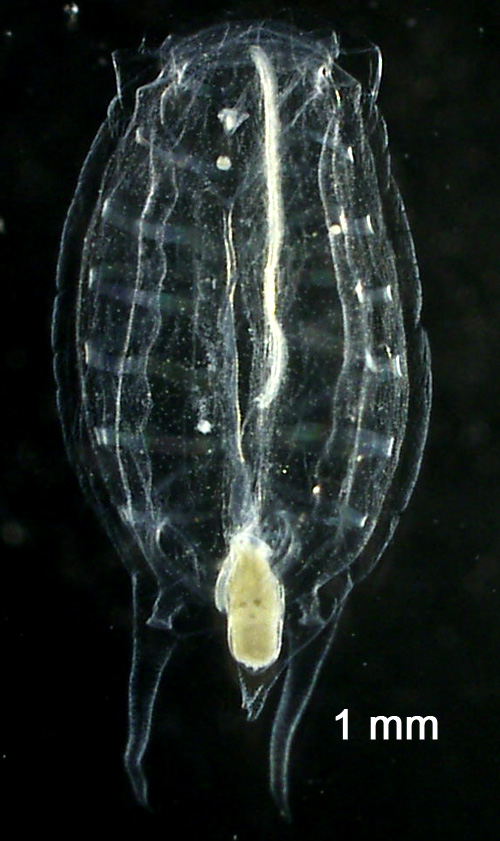
Thalia democratica(solitary w/ chain of zooids) 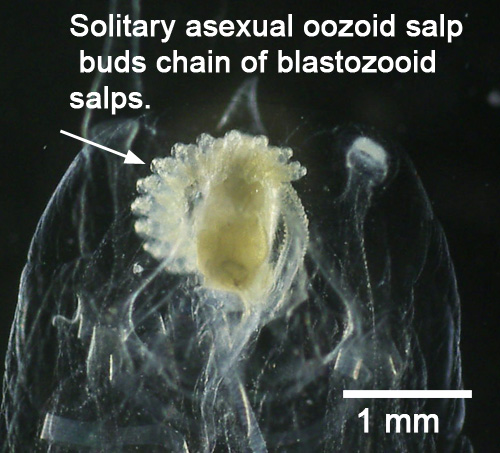
Thalia democratica(aggregate chain of zooids) 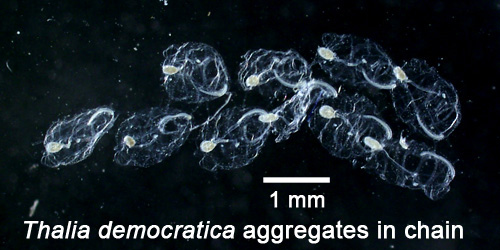

|